The Haredi Institute for Public Affairs is proud to publish updated demographic and employment data of the Haredi population in the Israeli capital for Jerusalem Day 2023. Over the past year, the institute has developed an innovative algorithm based on machine learning that is able to map Haredi educational institutions, characteristics and lifestyle, thus identifying optimally who is Haredi and who is not. The data presented below is based on administrative files of the Tax Authority, the Ministry of Education and the Population Authority.
Main Points:
- About 966 thousand residents live in Jerusalem, of which about 271 thousand are Haredi.
- The Haredi make up 28.1% of the total population in Jerusalem and 45.9% of the Jewish community in the city.
- The rate of Haredi in the city increases on average every year by 0.25%.
- The negative migration from the city in the Haredi sector is estimated at tens of thousands in the last decade – apparently due to housing prices.
- The Lithuanian denomination is the largest in the Haredi population in Jerusalem (117 thousand people).
- The neighborhood with the highest number of Haredi residents: Ramot.
- The Haredi population in the city is older compared to the rest of Haredi society in Israel – with an average age of 22.6 for men and 23 for women.
- The employment rate of Haredi society (ages 25-64) in Jerusalem stands at 42.2% among men and 73.8% among women.
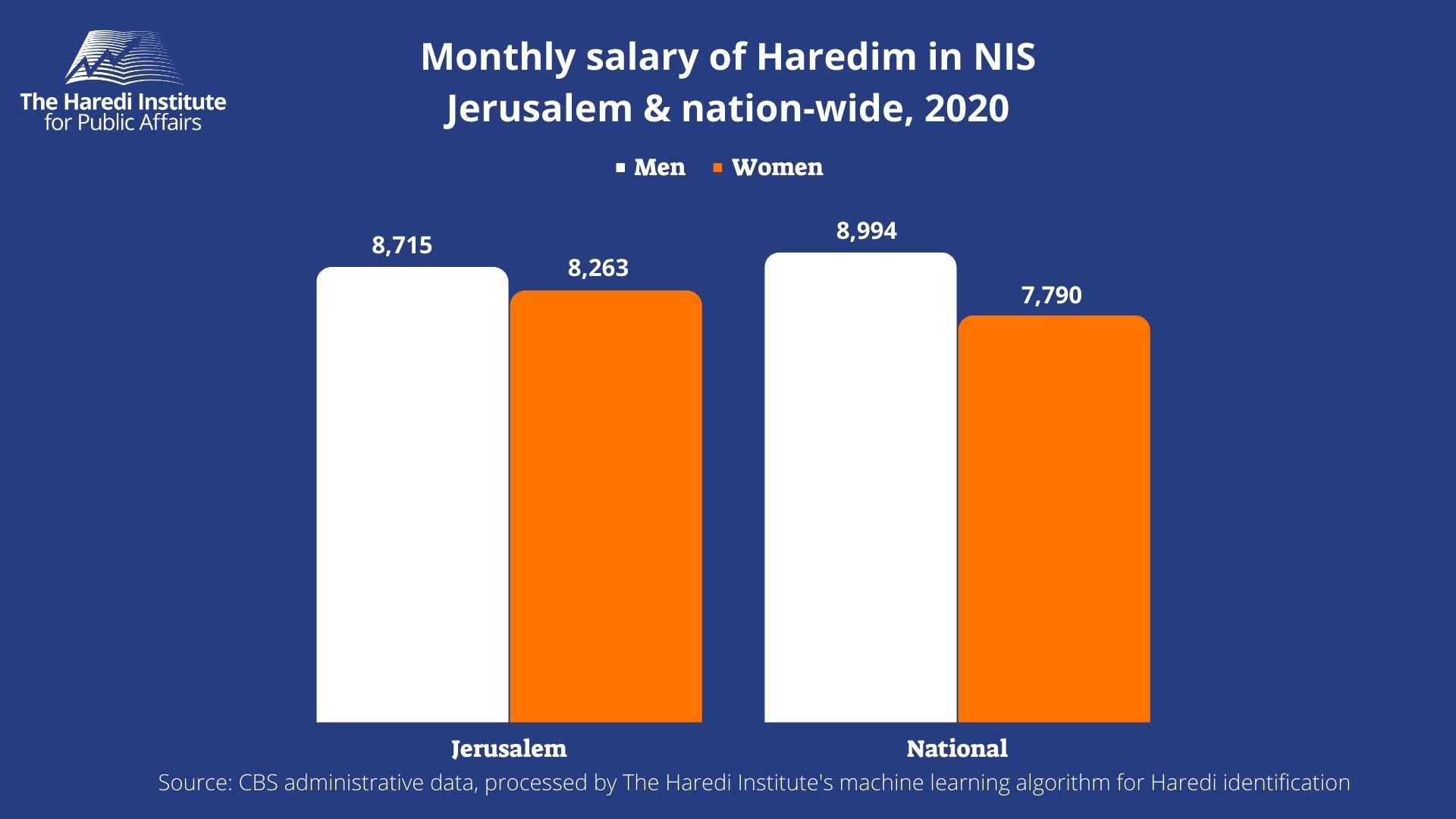
- The average monthly salary in Haredi society in Jerusalem is 8,715 NIS for men and 8,263 NIS for women.
Demography
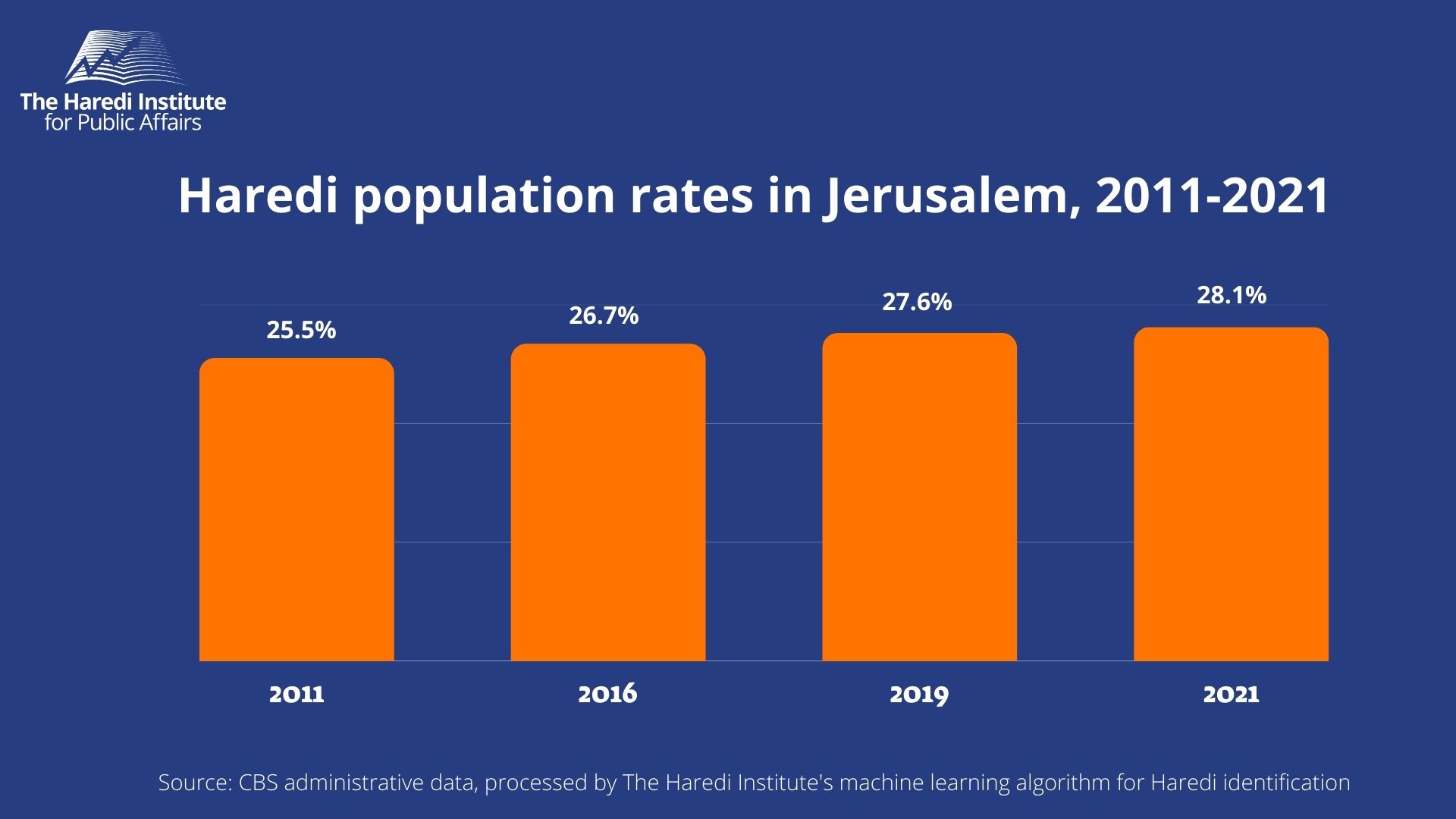
About 966,000 residents live in Jerusalem, of which about 271,000 are Haredi – who make up 28.1% of the total population in the capital and 45.9% of the total Jewish population, according to 2021 data. The proportion of Haredi living in the capital is 24.2% of all Haredi living in Israel.
The proportion of the Haredi population in the city has been increasing over the years, despite the migration of tens of thousands of Haredi from Jerusalem to other cities in Israel. Between 2011 and 2019, 59,026 Haredi left Jerusalem, compared to 76,558 of the city’s total population (including children born after 2011).
In 2011 the rate of Haredi in Jerusalem was 25.5%, in 2016 the number rose to 26.7%, in 2019 it climbed to 27.6% and as mentioned the latest figure from 2021 indicates a rate of 28.1%. In the last decade, the proportion of Haredi in the city has been increasing at a rate of 0.25% per year.
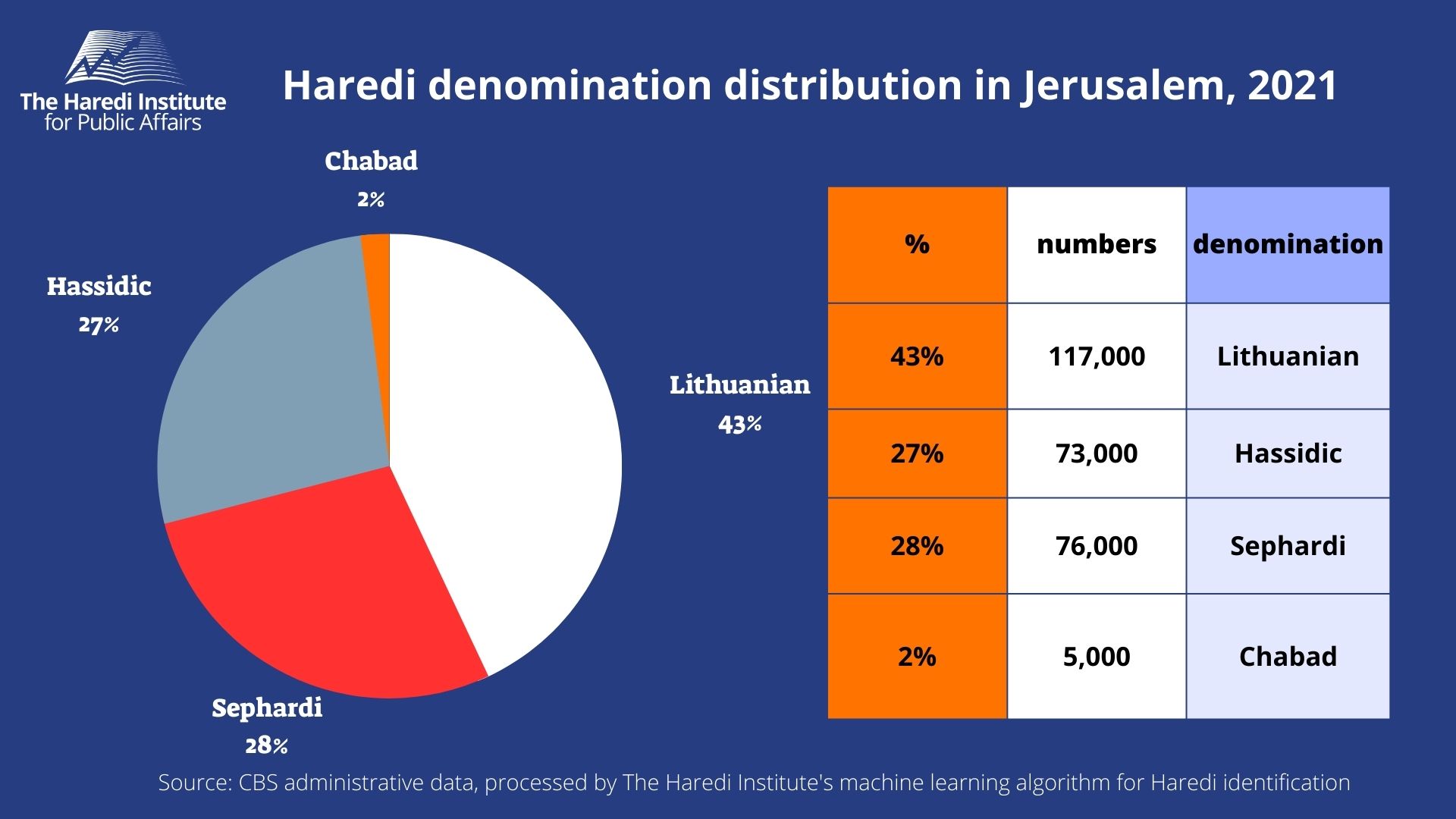
Distribution of Haredi society in Jerusalem according to denomination:
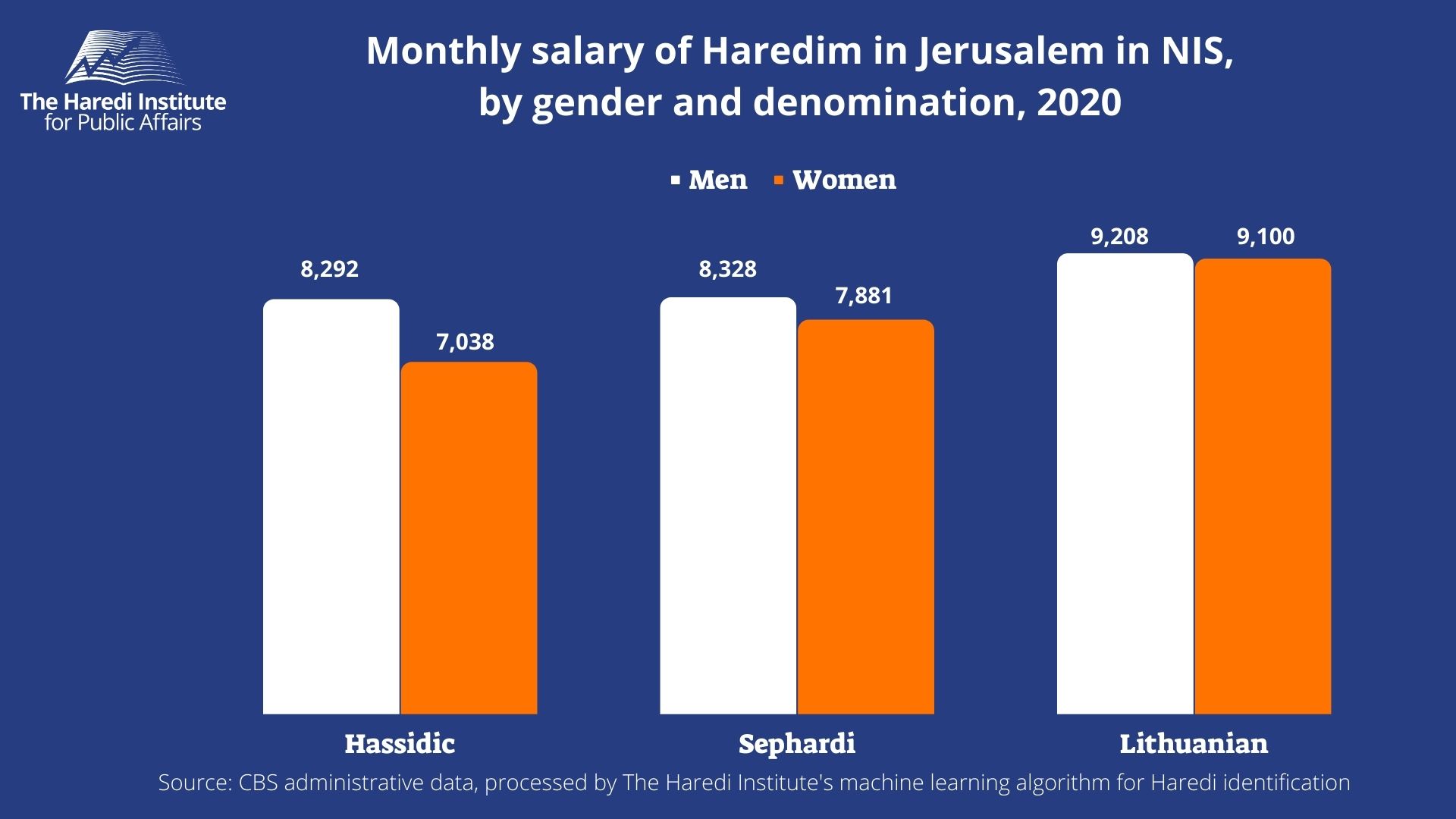
- Lithuanian – 117 thousand people (43% of the entire Haredi population in the capital)
- Chassidic – 73 thousand people (27% of the total Haredi population in the capital)
- Sephardi – 76 thousand people (28% of the total Haredi population in the capital)
- Chabad – 5 thousand people (2% of the entire Haredi population in the capital)
About 10% of the Haredi population in Jerusalem (mainly in the Hassidic denomination and some in the Lithuanian and Sephardic denominations) belong to the circles of the Edah HaChareidis (the Haredi council of Jerusalem)
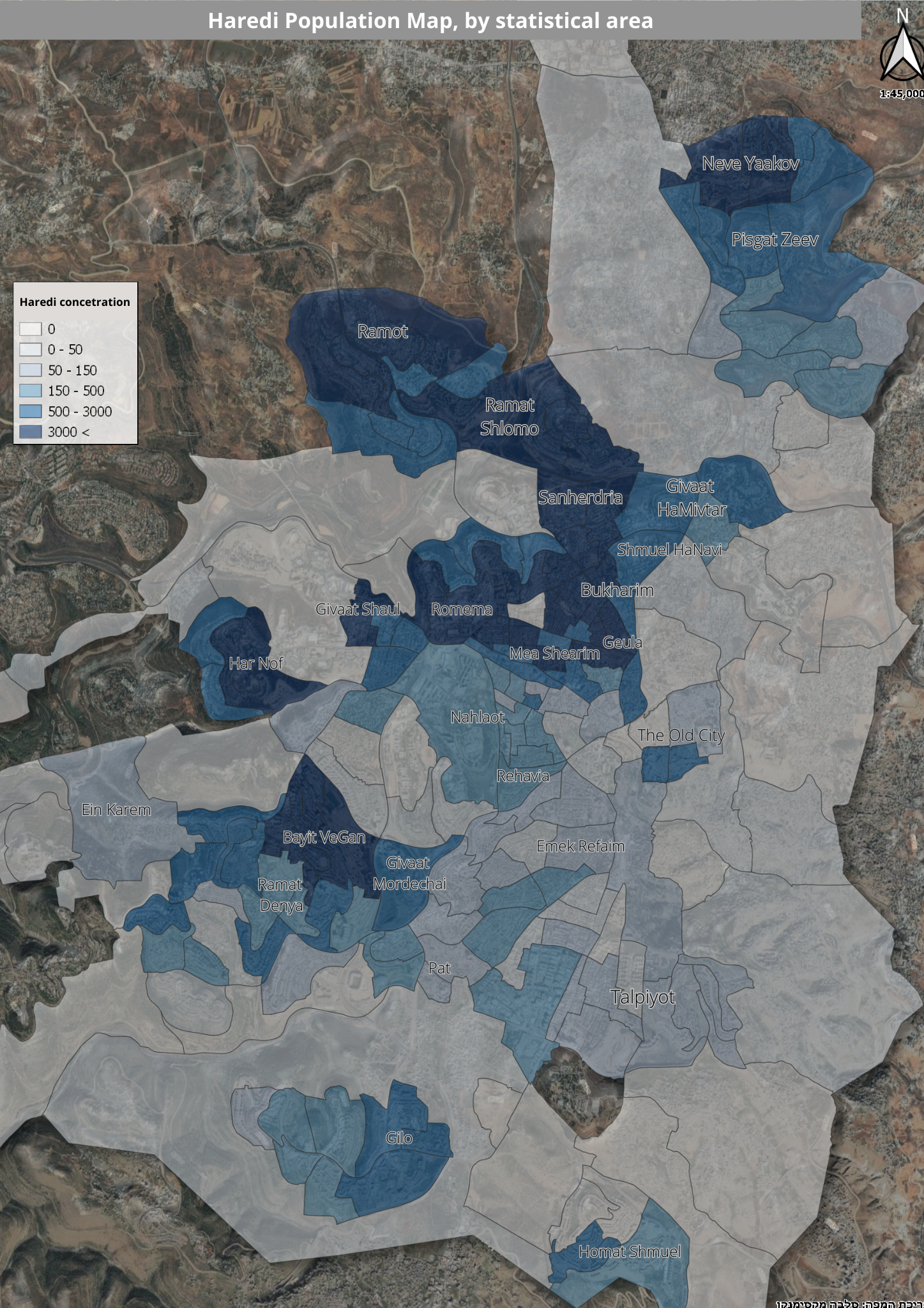
Distribution by neighborhoods
In 16 neighborhoods throughout Jerusalem have a solid Haredi majority of 75% or more: the Bukharim Quarter (96%), Romema (95), Geula (94%), Ramat Shlomo (94%), Mea Shearim (93%), Sanhedria (93 %), Beit Israel (93%) Shmuel HaNavi (92%), Mekor Baruch (89%), Har Nof (84%), Ma’alot Dafna (83%), Neve Ya’akov (82%), Ramot (79%), Bayit VeGan (78%), Givat Shaul (76%), Ramot Eshkol (75%).
Ramot is the neighborhood where the highest concentration of Haredim live in absolute numbers, with 40,100 of the neighborhood’s 51,100 residents being Haredim.
The neighborhoods after it on the list, with at least 10,000 Haredi residents (in descending order):
- Romema (25,900 Haredi residents out of 27,400 residents)
- Neve Ya’akov (21,700 out of 26,400)
- Bayit VeGan (17,300 out of 22,200)
- The Bukharim Quarter (15,700 out of 16,300)
- Har Nof (13,700 out of 16,181)
- Mea Shearim (11,500 out of 12,300)
- Shmuel HaNavi (10,900 out of 11,800)
- Beit Israel (10,400 out of 11,200)
- Ramat Shlomo (10,300 out of 10,900)
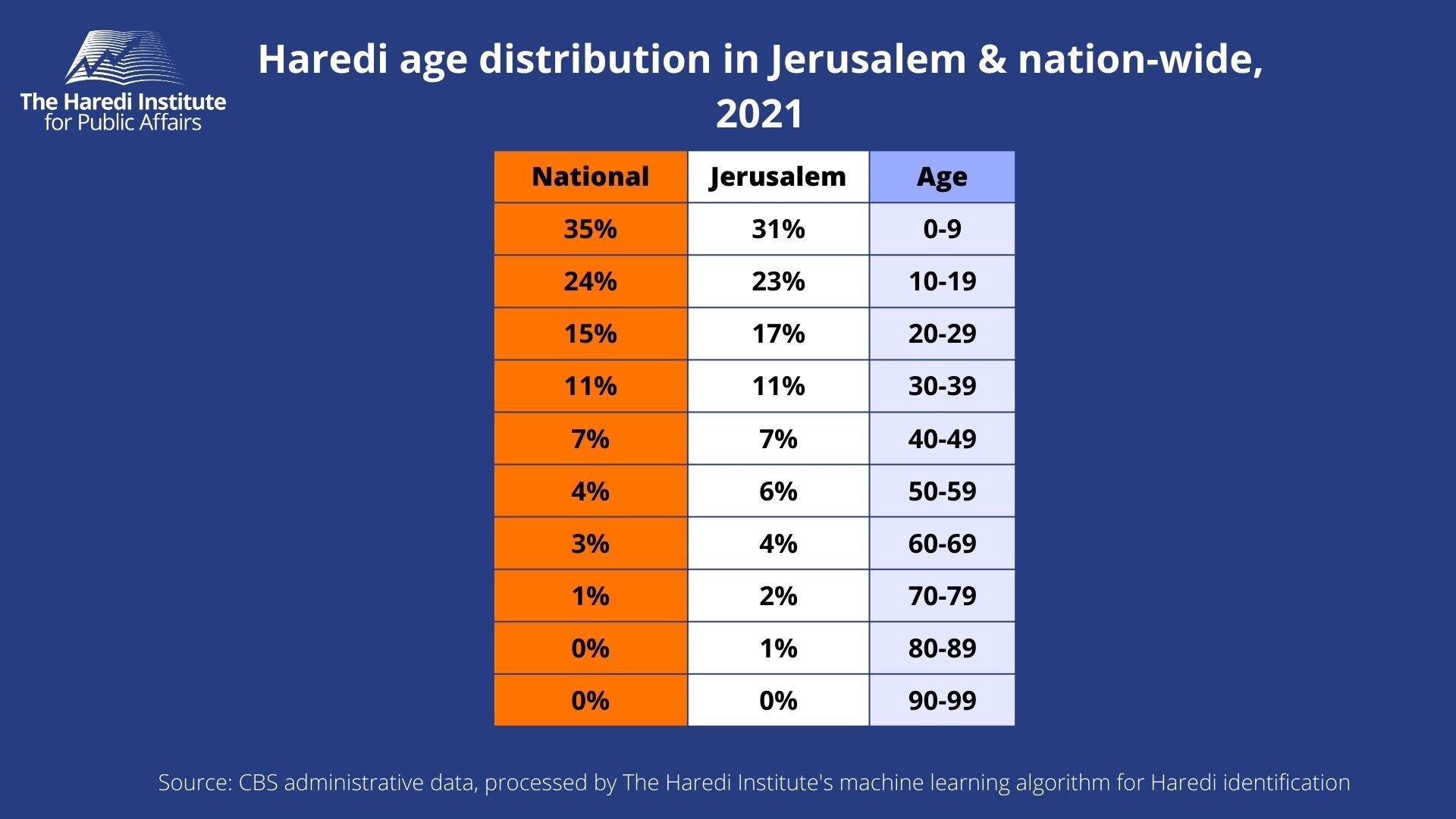
Older than younger
The Haredi society in Jerusalem is older than the rest of the Haredi population throughout the country. Consequently, the proportion of Haredi children in Jerusalem is lower than in the rest of the Haredi sector in Israel.
The average age for a Haredi in Jerusalem is 22.6 for a man and 23 for a woman, while in the rest of the country the average age for a Haredi is 20.2 (for both men and women). For comparison, the average age for non-Haredi men (including Arabs) in Jerusalem is 33.7 and 35.8 for women.
The proportion of children aged 0-9 in the Haredi population in Jerusalem is 31%, compared to 35% in the rest of the country. Also, the rate of children and boys aged 10-19 stands at 23% compared to 24% in the rest of the country. At the same time, the proportion of people aged 60 and over in Jerusalem stands at 7%, compared to 4% in the rest of the country.
Employment and Wages
As of the end of 2020, the employment rate in Jerusalem of the Haredi society (ages 25-64) stands at 42.2% among men and 73.8% among women, while the employment rate of the Haredi society in the rest of the country stands at 51.9% for men and 78.8% for women.
Haredim employment rate in the capital by denomination (as of 2020):
Lithuanian – 78% women, 38% men
Sephardi – 78% women, 46% men
Hassidic – 61% women, 44% men
The average monthly salary in Haredi society in Jerusalem (ages 25-64, as of 2020) is 8,715 NIS for men and 8,263 NIS for women. This is compared to the average salary of the Haredi society in the rest of the country, which is 8,994 NIS for men and 7,790 for women.
The CEO of the Haredi institute, Udi Ben Dror: “Jerusalem is a microcosm of Israeli society and it gives us a forecast of what Israeli society will look like in 30 years. The Haredi society is the great opportunity that Israeli society has, an opportunity that has not been realized so far. The great challenge for all of us is to plan the right policies and create solutions that will enable the joint life that will lead to the prosperity of the entire Israeli society.”
Dr. Eitan Regev, VP of Research and Data at the Haredi Institute: “Thanks to the special algorithm we developed, we know how to identify more accurately the Haredi population in Jerusalem and in Israel. From the data we were surprised to discover that in the last decade, between 2011-2019, Jerusalem lost approx. 135,000 residents (including children born to residents who left), of which almost 60,000 are Haredi (44%). Considering that the Haredi society makes up only about 28% of the city’s residents, this is a particularly high proportion of Haredi people who leave the city – probably due to the high cost of living and the difficulty in finding housing solutions at an affordable price.”

